A Guide to Flexible Conduit Fitting Parts
Leave a CommentIn order to effectively protect electrical wiring, both a flexible conduit and a liquid-tight seal are necessary.
Flexible Conduit is a tube used to route and protect wires and cables. It is typically made of metal or plastic.
A Liquid tight seal is a special type of fitting that is used to create a watertight connection between the conduit and an electrical box or enclosure. This type of seal is essential in preventing moisture from damaging the wiring. In addition, it helps keep out dust, dirt and other debris.
Together, a conduit and a liquid tight fitting provide an effective way to protect electrical wiring from the elements. When installed properly, a liquid tight seal will provide years of trouble-free service.
Types of Conduit Fittings
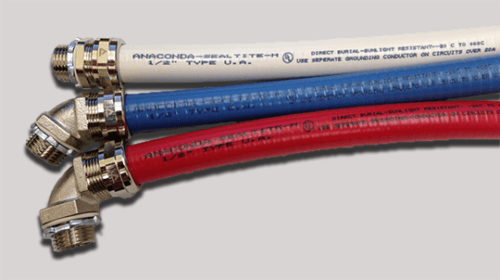
In many electrical applications, conduit fittings are crucial. Conduit fittings are available in various materials, Trade sizes and 45-degree, 90-degree or straight configurations.
When selecting conduit fittings, it is important to consider the application and the type of conduit being used. Operating conditions such as temperature, humidity and corrosion must also be taken into account. Safe electrical conduit fittings are described in the National Electrical Code (NEC) that is frequently updated to keep up with new technology and electrical safety requirements.
How to Choose the Right Conduit Fitting
Among available fittings, material, shape and finish are essential features.
The most common types of conduit fittings include:
- Straight: This allows conduit to be directly connected to the side of an enclosure.
- 45-degree: This allows wiring to take a slight bend when being connected between flexible conduit and an enclosure.
- 90-degree: This allows wiring to take a full corner bend, aligning conduit with the side of an enclosure.
Other types of flexible conduit fittings are less commonly used, including ground lug, strain relief, cord grips and ATEX (European Explosive Environment rated) fittings. All of these fittings serve different purposes, but they all play an important role in ensuring that electrical systems can be properly installed and maintained.
Conduit Fittings Assembly
Correct assembly of fittings on conduit is essential. Fitting components contribute to the liquid tight seal on conduit, so make sure each piece is properly installed before moving on to the next step.
- Make sure the end of conduit is smooth, without rough edges.
- Make sure fitting threads and the enclosure are clean and dry.
- Do not cross threads while assembling the fitting parts.
- Tighten the fitting to UL/CSA torque for a secure, liquid tight seal.
Here is a short instructional video to show how to cut conduit and install a Food Grade hygienic fitting.
ANACONDA SEALTITE® Fitting Features
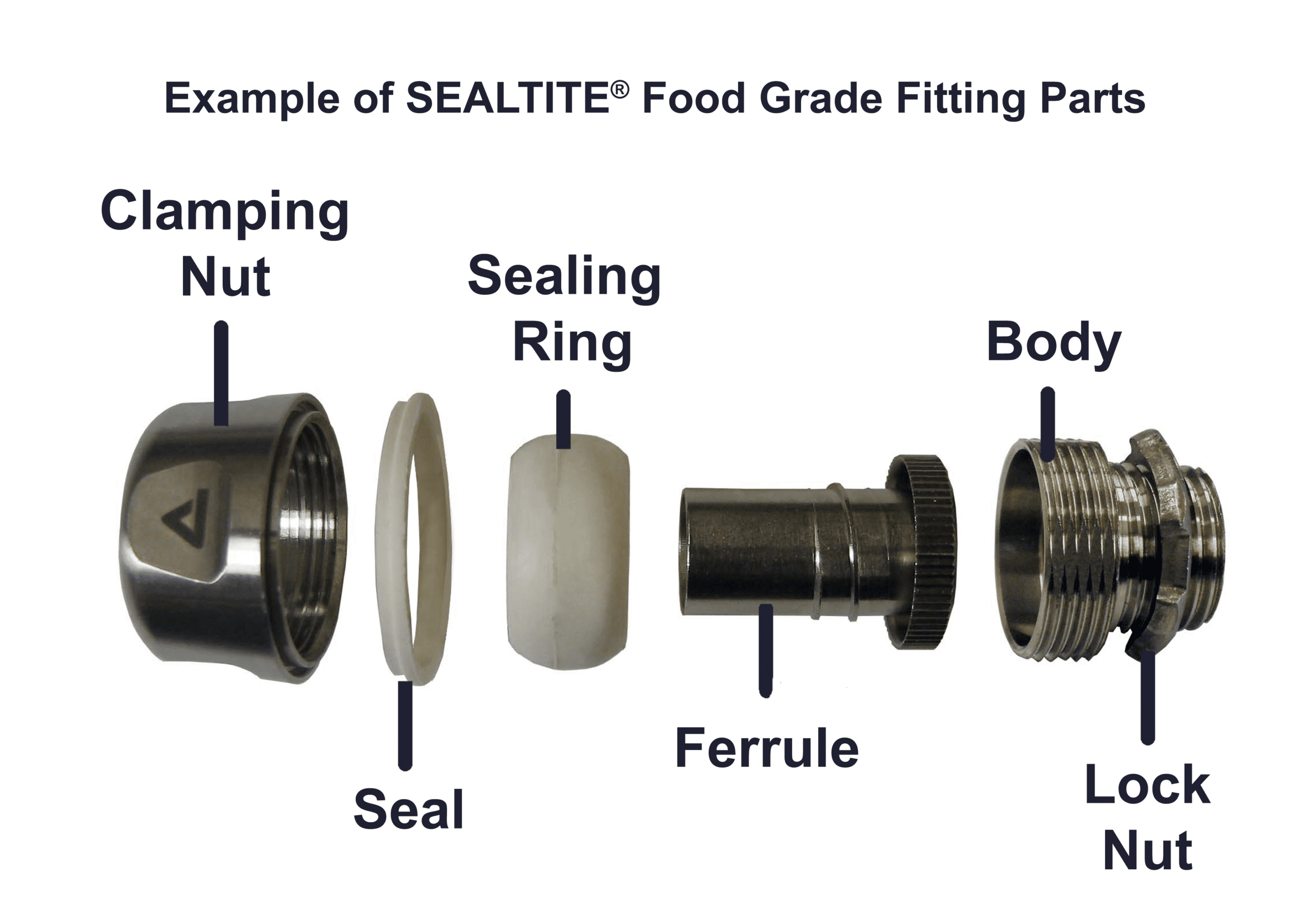
- Clamping or Gland Nut: This design constrains the sealing ring to firmly hold the conduit jacket.
- Sealing ring: The shape and flexibility of this polymer ring firmly holds the conduit when the nut and body are firmly tightened.
- Ferrule or Ground Ferrule: The threads and cap on the ferrule fit the conduit end and internal convolutions for a firm grip and liquid tight seal.
- Body: Internal geometry of the fitting body cup the sealing ring to constrain the conduit.
- Sealing Washer: Where installed, this washer seals the fitting against an enclosure.
- Lock Nut: The tiger claw lock nut resists loosening when the fitting is attached to an enclosure.
- Insulated Throat: Where installed, this polymer insulator prevents wires from chafing on the edge of the fitting.
- Enclosure Seal: Where installed, such as on hygienic fittings, this seal promotes a firm seal against an enclosure.
Conduit Systems from Anamet Electrical
Anamet Electrical, Inc. manufactures conduit systems with corrosion resistant, liquid tight, electrical conduit and fittings. Our products connect and protect electrical wiring in harsh operating conditions. Please visit to learn more about our UL listed Flexible Conduit Fittings , contact us to request a quote, and let us help you find the perfect fit for your next project.
Metallic vs Non-Metallic Flexible Conduits
2 CommentsFlexible conduit is pipe or tubing used to protect and route electrical wiring in a structure. They can be various materials, including metal or plastic.
There are two main types of conduit: metallic and non-metallic. Each has advantages and disadvantages to consider while choosing conduit for a particular application.
Metal conduit is usually made of aluminum or steel. It is strong and durable, making it ideal for applications requiring mechanical protection for wiring. However, metal conduit is more expensive than a non-metallic conduit and is subject to corrosion.
Non-metallic conduit is made of plastic, such as PVC or HDPE. Non-metallic conduit is less expensive than a metallic conduit and is not subject to corrosion. However, non-metallic conduit is not as strong or durable as metallic conduit and may not provide the same level of mechanical protection.
When choosing between metallic and non-metallic conduits, it is essential to consider the application’s specific needs. Cost, durability, flexibility, weight and temperature or corrosion resistance are important factors to consider. The right type of conduit will depend on the application’s particular requirements.
Now, let’s dive into the similarities between the two conduits.
Similarities among a metallic conduit and a non-metallic conduit
Metallic conduit and non-metallic conduit have these similarities:
- Both are composed of materials that are strong and durable, making them ideal for electrical wiring applications.
- Both types of conduit are designed to protect and route electrical wiring.
- Both metallic and non-metallic conduit are available in various common Trade sizes to accommodate different applications.
- Both are suitable for use in domestic, commercial, and industrial buildings and structures.
- Both protect against fire, mechanical damage and corrosion.
- Both may be rated for electrical safety applications according to the National Electrical Code (NEC).
- Both have adequate electrical field shielding and flexural stiffness (resistance to deformity).
Differences between metal conduits and non-metal conduits
Here are key differences between metal and non-metallic conduit to consider:
Non-metallic conduit
Here are some of the advantages of using non-metallic conduit:
- It can be used for fixture whips, data centers, electric signs and outdoor lighting, HVAC, pool and spas, and locations with exposure to sunlight and weather conditions.
- It is less expensive than most metal conduit.
- It is easy to cut at the site of installation.
- It is lighter weight than most metal conduit.
- It is more flexible than most metal conduit, making it easier to route through tight spaces.
- It may be installed in wet locations and buried in the ground or in concrete.
- It may be installed indoors, outdoors, under ground and above ground.
- PVC conduit may be recycled multiple times.
Here are some disadvantages in use of non-metallic conduit:
- It is not as resistant to crushing force, even though it may rebound from impact.
- Most non-metallic conduit is not rated for high or low temperature extremes
- It is not permitted in hazardous areas where the ambient temperature exceeds 50°C (122°F) or in applications where the conductor insulation temperature exceeds the rated temperature, such as extreme cold.
- It cannot be installed in plenum environments due its flammability and possibility for generating toxic smoke or fumes in a fire.
- It cannot be used without physical support along its installed length.
Metallic conduit
The following are the advantages of using metal conduits:
- Metal conduit is durable and can last many years with proper maintenance.
- Galvanized steel, aluminum, stainless steel, bronze and brass conduit is recyclable, making them a more sustainable option than other materials.
- It can withstand extreme temperatures and conditions, making it an ideal choice for protecting electrical wiring in harsh operating environments.
- It is resistant to impact and temperature changes, making it an ideal choice for protecting wiring in high-traffic areas or areas subject to extreme temperatures.
- It is made of non-combustible material, making it an excellent choice for protecting wiring for fire safety applications.
- It can be rated for electrical safety applications.
- A metallic conduit is easy to machine or fabricate, making it ideal for applications that require custom sizes or shapes.
- Extruded polymer jackets meet or exceed industrial chemical resistance requirements.
- Polymer jackets provide liquid tight protection allowing installation in wet conditions, or burial underground or in concrete.
- Polymer jackets provide low smoke or Halogen free protection of wiring.
- A integral bonding wire may be included in metal conduit, supporting NEC approved use in electrical connections.
However, using a metallic conduit also has some disadvantages, including:
- It costs more upfront to purchase the materials and install them.
- It does not offer full protection for circuits above and below ground against hazards, without a liquid tight jacket.
- It is heavier than a non-metallic conduit.
Flexible metallic & non-metallic conduits from Anamet Electrical
Key differences in these conduit types is material, durability and cost.
Metal conduit is more expensive than non-metallic conduit but it offers better protection from fire, pests, and extreme temperatures. They are also more durable and have a longer lifespan.
Non-metallic conduit is made of plastic or other material, less durable than metal. However, is it less expensive, lighter weight, more flexible and more corrosion resistant.
Anamet Electrical, Inc. has over 100 years of experience manufacturing quality flexible conduit for electrical wiring. Our liquid-tight metal and non-metallic conduit types are available for protecting mission-critical wiring from harsh operating conditions on land, at sea and in the air.
Our flexible metallic conduit and non-metallic conduit are available in various sizes and lengths. They can be custom-ordered to meet your specific needs.
If you’re looking for a high-quality, reliable, and durable conduit solution, look no further than Anamet Electrical. Contact us today to learn more information about our products and services.
Conduit in Plenum Elements: What You Need To Know
Leave a CommentPlenums are environmental air handling spaces in buildings. No flammable material should be installed in those building spaces, due to lessons learned about preserving life and preventing injury from fire. A short document describing what conduit may be used in various areas is available as a reference from ANAMET Electrical, Inc.: Conduit Allowed in Plenum Environments.
Follow approved building plans and local safety code if you are purchasing conduit or installing conduit in a building. In short, conduit cannot be installed in all building spaces, even though it protects wiring.
What you need to know
Flexible metal conduit (sometimes called FMC, Greenfield or Flex) is made of metal strip coiled in a continuous hose. The metal is resistant to flame. Another benefit of this conduit is that it can protect wiring from physical damage. In a building, wiring must often be put around tight corners, near exposed metal with sharp edges or other hazards.
What Is A Plenum?
A plenum space is a compartment or chamber in a building that circulates conditioned air for heating or cooling purposes. In order to ensure proper ventilation, plenum spaces are usually located between the ceiling and the floor above or between the floor and the crawlspace below. Under the floor plenum spaces are also often used for routing wiring and ductwork.
In order to protect against fire, any material placed in a plenum space must be fire-resistant and have low levels of toxicity when burned. This type of material is referred to as “plenum rated.” Conduit, cable, and other electrical equipment that is installed in a plenum space must be plenum rated to meet building code requirements.
The word “plenum” is derived from the Latin word for “full.” Plenums were originally designed to be filled with air in order to provide more efficient ventilation. However, modern plenums may be insulated, only partially filled with air, in order to prevent noise from circulating or being amplified in the space. Although plenums can be found in all types of buildings, they are most commonly used in office buildings and schools.
Plenum Cable and Plenum Conduit
- Plenum cable is made with a special jacket that helps to protect the wire from fire. This is because plenum spaces often have a lot of oxygen, which can make them more susceptible to fire.
- Here are a few limitations put on flexible metal conduit for plenums. 1) Lengths are not to exceed 1.2 meters (4 feet). 2) No conduit with an overall nonmetallic covering shall be installed. 3) Only fire resistant metal is allowed, which protects wires from heat and fire.
- When choosing materials for a plenum space, it is important to choose products rated for use in these spaces. This ensures the safety of the building and the people who use it.
Cable vs. Conduit
- You may be allowed to install non-plenum cables in plenum areas depending on your building code requirements, if run through a plenum rated conduit.
- With plenum rated cable, there is no need for a conduit. Plenum rated cable is usually flame retardant, made with special plastics to prevent smoke or toxic fumes.
- Determine where wiring must be installed in a building, then specify the plenum rated cable or conduit.
Guidelines for Using Electrical Conduit in Plenum Environments
The National Electrical Code (NEC) serves as a guide that may be adopted or adapted by local jurisdictions for electrical safety and building codes. The NEC is frequently updated to address changes in technology and lessons learned in electrical and fire safety. Contact your local authority for current standards in electrical wiring installation. There are finer definitions for plenum environments in the NEC, promoting safety with new technology, such as information technology systems and their requirements. For ANAMET Electrical, Inc. support for safety see: Conduit Allowed in Plenum Environments.
Electrical Conduit, Fittings, and Accessories from Anamet Electrical
Anamet Electrical, Inc. is your one-stop shop for conduit systems. We offer a wide range of products that meet national and international fire safety requirements, among commercial, industrial and residential applications. Our team of experts can assist you in finding the right product to meet your needs.
Contact us today to learn more about our products and how we can help you with your next project.